The Internet of Things (IoT) serves as a comprehensive, global network linking a variety of digital devices. These devices communicate with each other through sensor networks. For example, a smart thermostat can seamlessly integrate with your home’s HVAC systems. The convenience, security, and precision enabled by IoT are beneficial across multiple sectors.
Many banks are adopting IoT technologies to enhance customer service and expand their market presence. The applications of IoT in the banking sector are both intriguing and far-reaching, with more innovations on the horizon. The integration of IoT is making banking increasingly user-friendly and secure.
In this article, we will explore the impact of IoT on banking, discuss its advantages, and look at how leveraging trends in IoT banking can give you a competitive edge.
What is IoT in Banking?
IoT in banking refers to the network of interconnected IoT devices that gather and transmit data, which is then processed on either a cloud-based or on-premise server to enhance customer and banking professionals’ experience.
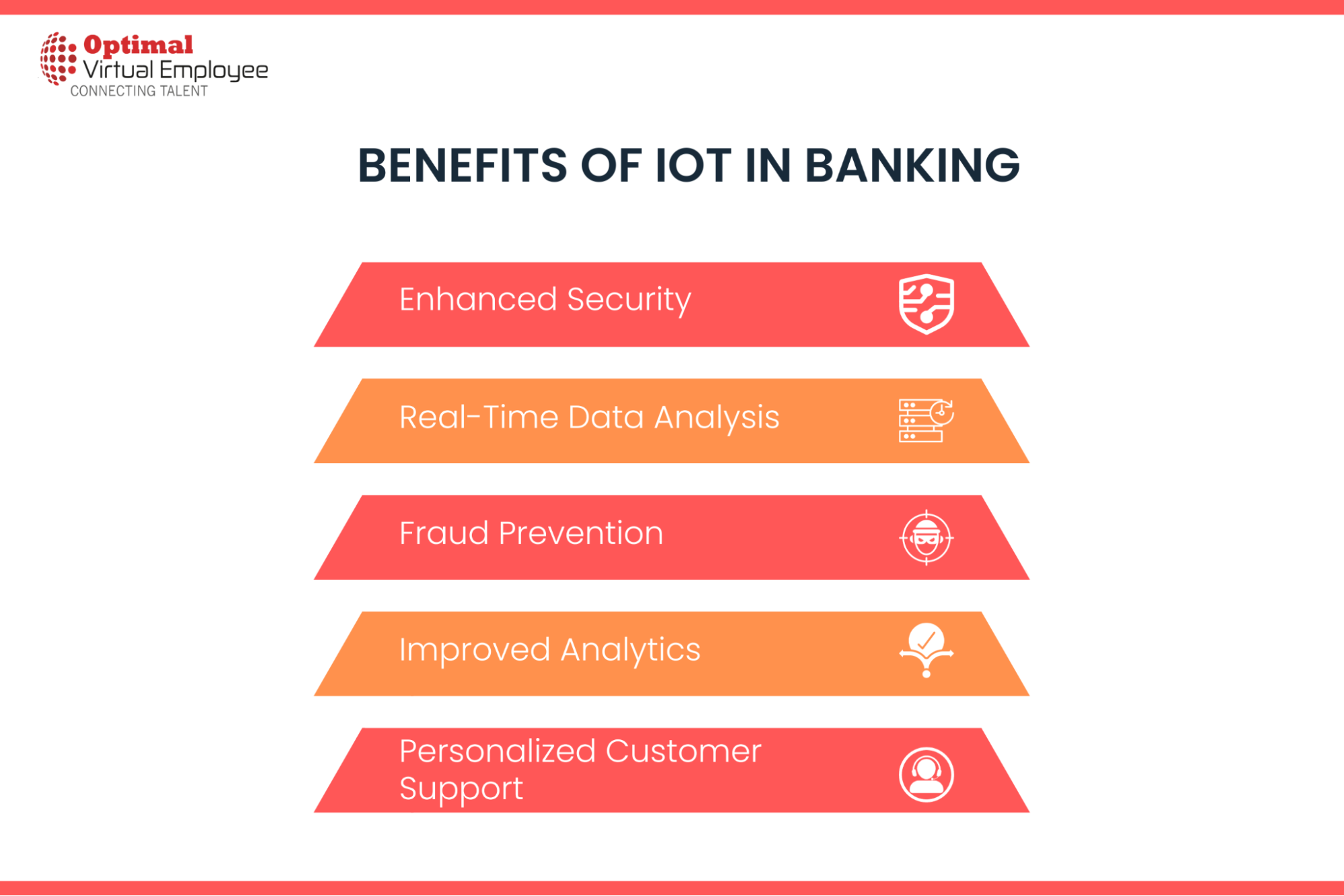
Advantages of IoT in Banking
Using IoT in banking has numerous benefits, some of which are listed below:
Enhanced Security
By integrating CCTV cameras, 24/7 security surveillance, intelligent alarm systems, and other technology focused on security, banks can significantly bolster the safety of their branch locations. IoT comes into play by facilitating the remote management and connectivity of these smart devices. This enables security personnel to quickly secure the branch or take other critical actions if a threat is detected.
Real-Time Data Analysis
IoT devices collect data in real-time from various banking touchpoints. This allows banks to assess customer needs dynamically, regardless of time or location. For instance, banks could estimate the wait time for customers in line or even alert customers when their account balances are nearing zero. The benefit is that real-time data enables banks to offer services that are precisely tailored to current conditions.
Fraud Prevention
The prevalence of banking fraud is on the rise worldwide, but IoT has the potential to combat this issue. Smart devices have already enhanced the security around transactions; for example, mobile phones now require biometric authentication for transactions to proceed. Another method involves sending an authentication code to customers’ phones, which must be entered to confirm online purchases.
Lastly, online banking apps that send notifications for every transaction are another example of IoT’s role in identifying and reducing fraud. This feature allows users to closely monitor each transaction and promptly report any unrecognized activities as fraudulent.
Improved Analytics
IoT provides banks with up-to-date data on projects or individuals they are financing, allowing for more accurate ROI calculations. For example, banks can use data from satellites and street cameras to gauge nearby economic activity. Other applications include:
– For consumer loans, banks can analyze data from various apps and sensors to gain a detailed insight into the borrower’s spending habits.
– In the securities sector, banks can utilize data from multiple analytics platforms to compare trading volumes between publicly and privately issued bonds.
Personalized Customer Support
By leveraging data from mobile apps, websites, and other platforms where transactions occur, banks can offer personalized services to each customer based on their transaction history. These personalized services could include tailored budgets and financial advice.
Diversified Offerings
Modern banking goes beyond just money and asset management. Lately, banks have begun utilizing data from customers’ smart devices like smartwatches to track their fitness levels. Based on this data, banks can reward customers for maintaining healthy lifestyles by offering incentives such as cash-back rewards or reduced interest rates.
Card-Free Transactions
Mobile banking apps now offer seamless integration with credit and debit cards, simplifying the transaction process. This allows customers to make contactless payments using only their smartphones. This feature has been especially valuable during the pandemic, as it helps to maintain cleanliness in stores and other high-traffic areas.
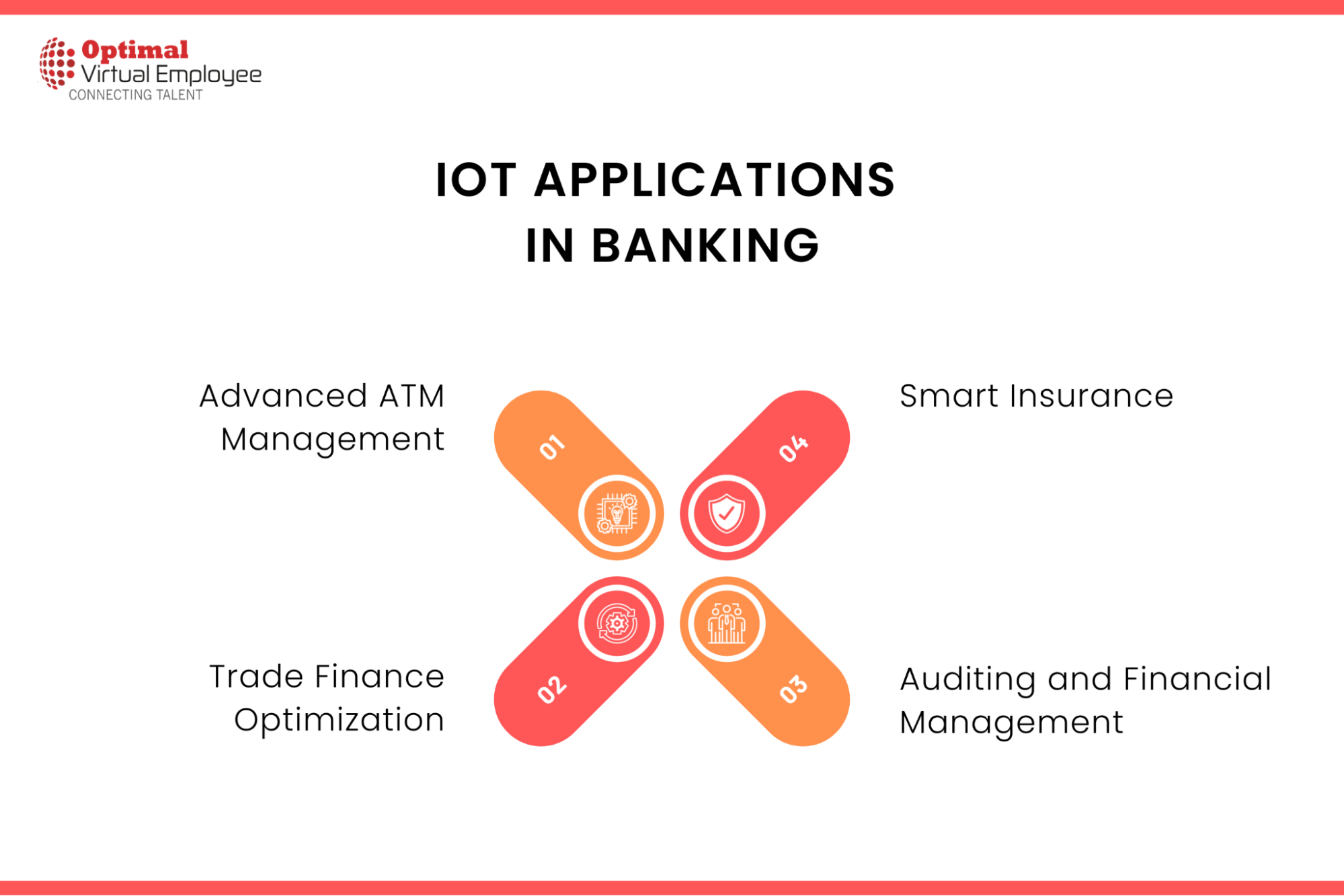
IoT Applications for Smarter Banking and Finance
Intelligent Branches
IoT solutions in smart branches enhance the customer experience by monitoring queue lengths and notifying customers of wait times or directing them to available service counters. These smart branches can also share customer data to optimize operations and reduce staffing needs.
Advanced ATM Management
IoT-enabled ATMs allow banks to observe consumer behavior, identify usage patterns, and strategically place new ATMs based on demand. Information from IoT sensors, such as room temperature and lighting, can help switch ATMs to energy-saving modes. Real-time monitoring ensures timely management of issues like skimming devices, card reader malfunctions, or cash shortages.
Trade Finance Optimization
For banks involved in trade finance, IoT provides real-time data that enhances visibility into the physical aspects of the trades they are financing. This data enables banks to manage funds more effectively, refine their financing strategies, and assess risks more accurately throughout the trade cycle.
Smart Insurance
IoT devices monitor the condition of insured assets and alert insurance companies to any irregularities, enabling timely intervention to mitigate risks. The data collected helps insurers predict potential incidents and formulate preventive measures. For example, an insurer might detect impending asset failure and alert the policyholder before any damage occurs, reducing the number of insurance claims and preventing fraud.
Auditing and Financial Management
IoT facilitates seamless integration between a client’s payment systems and accounting software, automating routine tasks like data entry, reconciliation, and invoicing. It empowers accountants with real-time financial data, providing them with accurate insights into business operations to elevate their advisory roles. Additionally, IoT enhances auditing by improving transparency and automation, enabling accountants to instantly track transactions and manage audit trails, making it easier to identify irregularities and prevent fraud.
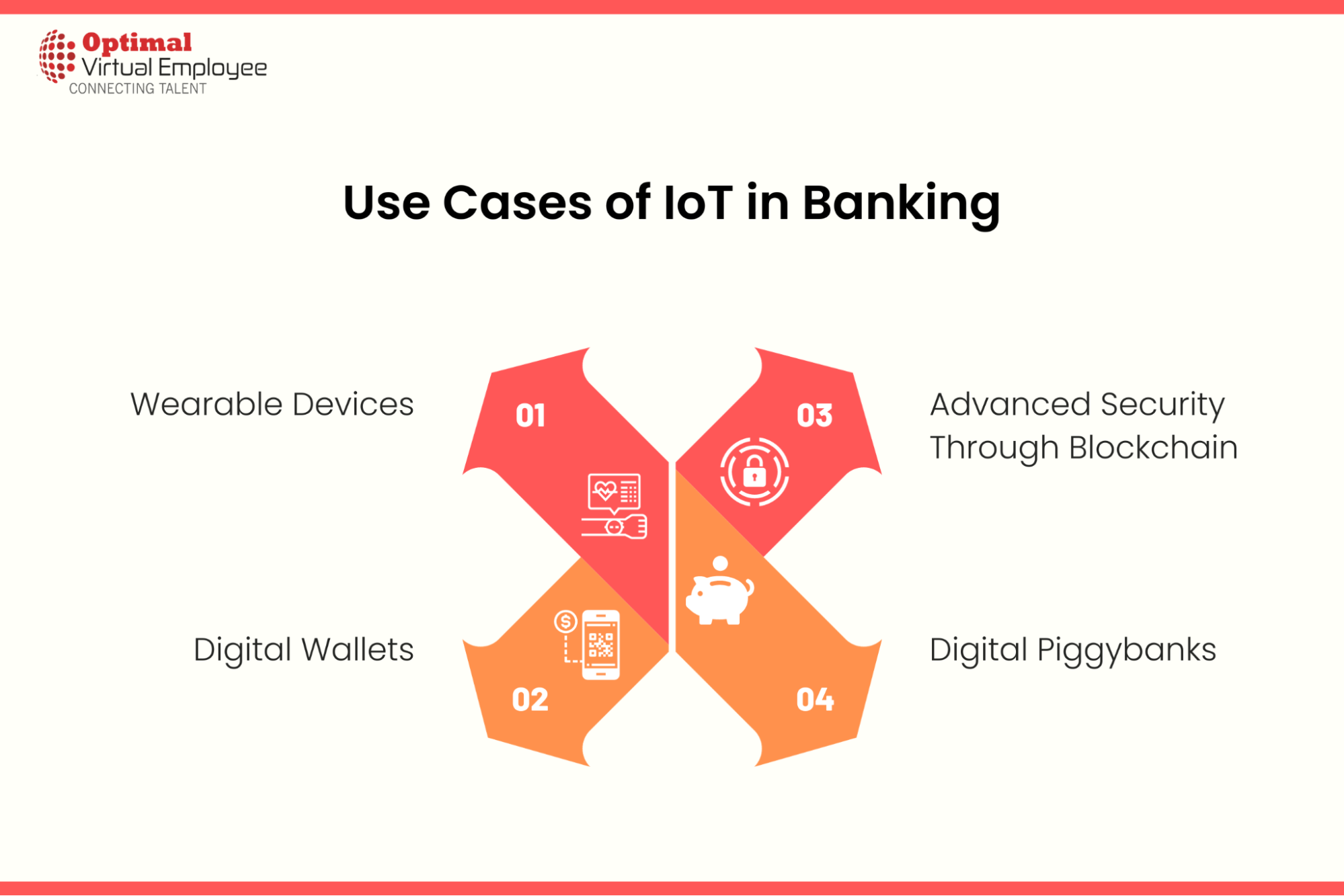
Use Cases of IoT in Banking
Here are four key IoT applications in banking:
Wearable Devices
Many people use smartwatches and wristbands for various purposes. Banks can enhance user experience by creating apps compatible with these wearables. Users can check their heart rates, manage work emails, and perform financial transactions all from the same device.
These wearables also offer an added layer of security by sending notifications to users whenever there’s a withdrawal from their accounts. Customers can even interact with their banks directly through the wearable device, making multitasking easier and saving time. Convenient access to financial information via these smart devices can also help users meet their financial goals and save money.
Digital Wallets
Monetary systems have seen significant changes over the years. From trading in actual gold to bank-backed currencies, and eventually, to card-based digital funds, the transformation has been substantial. Digital wallets are the latest evolution, allowing users to access their money simply by opening an app and tapping their smartphones.
Digital wallets offer immense convenience, reducing the number of items people need to carry daily. In an era where almost everyone has a smartphone, adapting banking technology for mobile use has been one of the most practical IoT advancements in the sector. Of course, users must ensure the security of their mobile devices for this payment method to remain secure.
Advanced Security Through Blockchain
In the near future, blockchain could revolutionize the banking industry by enabling secure, middleman-free transactions, traditionally a role played by banks. This technology is especially useful for international transactions as every activity is permanently logged, making fraud more difficult to commit. By embracing blockchain, banks can reduce costs while enhancing transparency and security for customers. Moreover, blockchain can aid in more secure customer identification and asset protection.
Digital Piggybanks
Another innovation in banking brought by IoT is the concept of smart piggy banks. Modern banks are offering digital piggybank services to help customers set and achieve financial goals quickly. This interactive platform is a great way for children to learn about money management. Unlike traditional piggybanks, these virtual versions come with interest rates to accelerate money growth.
For adults, the term “investment banking” might sound daunting, but “digital piggybank” has a simpler, more approachable feel. IoT technology allows banks to rebrand in this way, attracting a broader customer base and generating mutual financial benefits for both banks and their clients.
Conclusion
The financial sector is currently experiencing a technological renaissance, with new innovations being introduced and trialed frequently. These range from advanced machine learning algorithms to blockchain solutions, each promising to redefine traditional banking practices. However, not all these technologies manage to gain traction or make a substantial impact on the industry.
Among the burgeoning technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT) stands out as a game-changer for banking. IoT has the potential to significantly shift the dynamics of the industry by enhancing customer experience, automating operations, and introducing new levels of security. Its applications in smart banking, real-time data analytics, and asset management indicate that IoT isn’t just a passing trend, but rather an integral component that can reshape the future of banking.